スレッドはひとつのプログラム内で複数の処理を同時並行的に実行するための仕組みで、スレッドの処理内容を書く際にラムダ式が使われることが多いです。
ここではJavaでスレッドを利用する方法について学びます。
まず最初にスレッドを作成します。
ラムダ式を使ってこのスレッド内で実行する処理内容を書きます。
var スレッド名 = new Thread( ()->{
処理内容
});
次に作成したスレッドを実行します。
するとスレッドがいま動いているプログラム(メインスレッド)とは別に並行して動き始めます。
スレッド名.start()
実行したスレッドの処理が終了するのを待ちたい時は次のように書きます。
スレッド名.join()
ではスレッドを使った例を示します。
次のソース1を実行するとスレッドが2つ(thread1とthread2)作られます。
thread1は0.1秒おきに"thread1"と表示します。
一方thread2は0.5秒おきに"thread2"と表示します。
import java.lang.Thread;
public class Main {
// msecだけ停止する関数
public static void sleep(int msec){
try{
Thread.sleep(msec);
}
catch(InterruptedException e){}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
var thread1 = new Thread( ()->{
for(var i = 0; i < 5; ++i ){
sleep(100);
System.out.println("thread1");
}
});
var thread2 = new Thread( ()->{
for(var i = 0; i < 5; ++i ){
sleep(100);
System.out.println("thread2");
}
});
// 各スレッドを実行
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
// 各スレッドが停止するまで待つ
try{
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
}
catch(InterruptedException e){}
}
}
結果は次のようになります。
2つのスレッドが並行して動いていることがわかります。
thread1 thread2 thread2 thread1 thread2 thread1 thread2 thread1 thread1 thread2
「デッドロック」とは、複数のスレッドが同時に同じリソース(ファイルやメモリや周辺機器などの資源)を利用しようとしたときに、互いにリソースの開放待ち状態におちいって膠着状態となってしまう状況を言います。
例えば下のソース2を実行してください(ちょっと長いですが、main関数のところだけ見れば何をやっているのか分かると思います)。
import java.lang.Thread;
public class Main {
static int resource1 = 0;
static int resource2 = 0;
// msecだけ停止する関数
public static void sleep(int msec){
try{
Thread.sleep(msec);
}
catch(InterruptedException e){}
}
// リソース1をロックする関数
public static void lock_resource1(){
while(resource1 == 1) sleep(10); // リソース1のロック解除待ち
resource1 = 1;
System.out.println("リソース1 ロック");
sleep(10);
}
// リソース1のロックを解除する関数
public static void unlock_resource1(){
resource1 = 0;
System.out.println("リソース1 ロック解除");
}
// リソース2のロックを解除する関数
public static void unlock_resource2(){
resource2 = 0;
System.out.println("リソース2 ロック解除");
}
// リソース2をロックする関数
public static void lock_resource2(){
while(resource2 == 1) sleep(10); // リソース2のロック解除待ち
resource2 = 1;
System.out.println("リソース2 ロック");
sleep(10);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
var thread1 = new Thread( ()->{
System.out.println("thread1 開始");
// リソース1 → リソース2の順にロック
lock_resource1();
lock_resource2();
// リソース1と2を開放
unlock_resource1();
unlock_resource2();
System.out.println("thread1 終了");
});
var thread2 = new Thread( ()->{
System.out.println("thread2 開始");
// リソース2 → リソース1の順にロック
lock_resource2();
lock_resource1();
// リソース1と2を開放
unlock_resource1();
unlock_resource2();
System.out.println("thread2 終了");
});
// 各スレッドを実行
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
// 各スレッドが停止するまで待つ
try{
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
}
catch(InterruptedException e){}
}
}
結果はデットロックします。
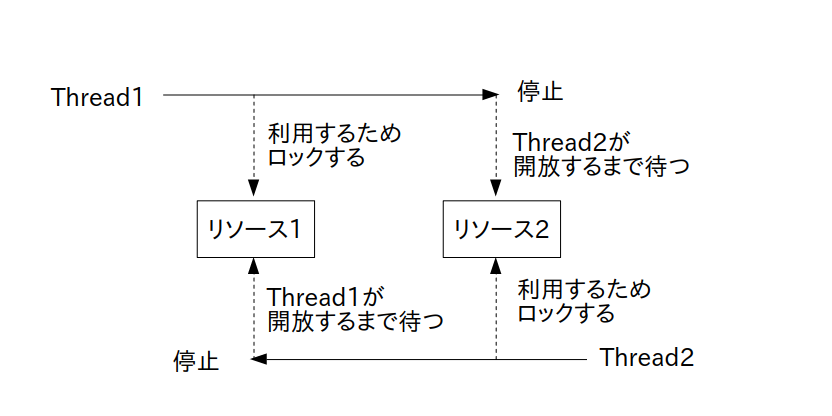
その理由は図1に示す様に、thread1はリソース2、thread2はリソース1の開放の待ち状態になって停止するためです。
thread1 開始 リソース1 ロック thread2 開始 リソース2 ロック (デッドロックして固まる!)

デッドロックを防止するためには「排他処理」をおこなって、あるリソースを同時に複数のスレッドが利用しないようにする必要があります。
排他処理をおこなうことで、特定のリソースを利用するコード部分(「クリティカルセクション」といいます)をひとつのスレッドが実行中は、他のスレッドはそのリソースにアクセスできなくなります。
Javaで排他処理をおこなう方法はいくつかあるのですが、今回は最もシンプルな synchronized を使った方法を見てみましょう。
例えば以下のコード3を見てください(やはり長いですが、main関数だけ見ればだいたい分かります)。
import java.lang.Thread;
public class Main {
// ロック用インスタンス作成
private static final Object lock = new Object();
static int resource1 = 0;
static int resource2 = 0;
// msecだけ停止する関数
public static void sleep(int msec){
try{
Thread.sleep(msec);
}
catch(InterruptedException e){}
}
// リソース1をロックする関数
public static void lock_resource1(){
while(resource1 == 1) sleep(10); // リソース1のロック解除待ち
resource1 = 1;
System.out.println("リソース1 ロック");
sleep(10);
}
// リソース1のロックを解除する関数
public static void unlock_resource1(){
resource1 = 0;
System.out.println("リソース1 ロック解除");
}
// リソース2のロックを解除する関数
public static void unlock_resource2(){
resource2 = 0;
System.out.println("リソース2 ロック解除");
}
// リソース2をロックする関数
public static void lock_resource2(){
while(resource2 == 1) sleep(10); // リソース2のロック解除待ち
resource2 = 1;
System.out.println("リソース2 ロック");
sleep(10);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
var thread1 = new Thread( ()->{
synchronized (lock) {
// ここからクリティカルセクション
System.out.println("thread1 開始");
// リソース1 → リソース2の順にロック
lock_resource1();
lock_resource2();
// リソース1と2を開放
unlock_resource1();
unlock_resource2();
System.out.println("thread1 終了");
// ここまでクリティカルセクション
}
});
var thread2 = new Thread( ()->{
synchronized (lock) {
// ここからクリティカルセクション
System.out.println("thread2 開始");
// リソース2 → リソース2の順にロック
lock_resource2();
lock_resource1();
// リソース1と2を開放
unlock_resource1();
unlock_resource2();
System.out.println("thread2 終了");
// ここまでクリティカルセクション
}
});
// 各スレッドを実行
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
// 各スレッドが停止するまで待つ
try{
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
}
catch(InterruptedException e){}
}
}
synchronized (lock) で囲まれた部分が各スレッドのクリティカルセクションとなり、他のスレッドがクリティカルセクションを実行中はクリティカルセクション内に入れなくなります。
よって実行結果は以下の通り、thread1→thread2の順に実行されてデッドロックが回避されます。
thread1 開始 リソース1 ロック リソース2 ロック リソース1 ロック解除 リソース2 ロック解除 thread1 終了 thread2 開始 リソース2 ロック リソース1 ロック リソース1 ロック解除 リソース2 ロック解除 thread2 終了